MRI
What is an MRI?
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body in both health and disease. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, radio waves, and field gradients to generate images of the inside of the body.
MRI is widely used in hospitals and clinics for medical diagnosis, staging of disease and follow-up without exposing the body to ionizing radiation.
What should I expect?
The technologist will take you into the MRI suite where you will be positioned on the MRI scan table. A coil, which functions as an antenna to receive the scan information, will be placed under, beside, or around the area to be scanned. You will be given hearing protection, as the scanner is very loud during imaging. A “zero point” will be established, and the table will move that point into the middle of the scanner. You will notice that a light will be on, a fan is on, and both ends of the machine are open. The table may move in farther or back out a little during the exam, but it never moves up or down once you are inside the machine.
The technologist begins the scan at the scan console on the other side of the window. You are always within sight of the technologist, and you can be heard and reached within moments if you were to need us. It is crucial that you hold still during the scan and continue to maintain that position between scans. Moving during the scan causes blurred images, and moving between scans causes the computer to scan in the wrong area.
The noise will last typically from one to six minutes per series, and a minimum of 4 series are required per exam, with some exams requiring up to about 6 or 8 series.
If your doctor ordered a contrast injection, approximately two-thirds of the exam will be completed, then you will be brought out of the scanner for an MRI contrast to be injected into a vein in your arm. The contrast is a gadolinium compound that affects abnormal tissues and causes them to appear “enhanced” compared to the images done before the injection. Once the injection is complete, you will go back into the scanner for the final third of the exam.
What can I do to prepare?
Prior to your MRI scan, you will be asked a series of questions that will determine if you are a candidate for an MRI exam. You will be asked, for example, if you have:
A pacemaker/defibrillator
Shunts or stents
Certain implants, such as ear implants, penile implant, breast tissue expanders, or a nerve stimulator
Bone growth stimulator
Metal fragments in your eyes
And a number of other metal- or electronics-related questions
Not all items on the list are dangerous, but some are. If you have a pacemaker, even an MRI conditional pacemaker, you will not be an MRI candidate at Fort Payne Imaging. MRI conditional pacemakers require specific monitoring devices during the exam that can only be done at large facilities. Other concerns about metal or implants will be discussed during the scheduling process. Once you are cleared for internal metals or potentially hazardous objects, you will be instructed to change clothing to remove zippers, snaps, etc. that may interfere with your exam.
For some exams, females will be required to remove a bra if it has the hook closure and/or underwire. Wearing a metal-free sports bra may be your preference on test day. You will be issued a locker to use during the exam, where you will lock personal belongings for safekeeping during the test. Your purse and/or wallet, keys, phone, tablet, etc. will be placed in the locker with your clothing. Your hearing aids must be removed, as well as your watch. Other jewelry will be removed if it could interfere with the image quality. Not all objects interfere, so detailed instructions will be given, always with your safety as the primary concern.
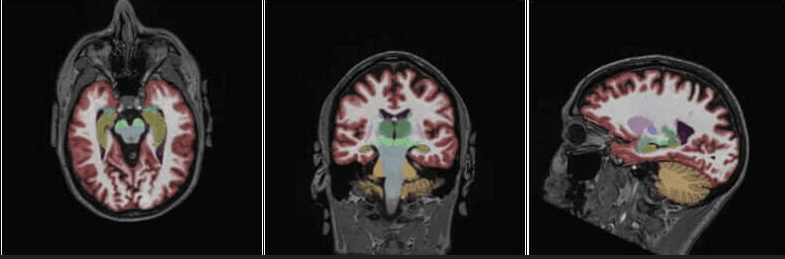
NeuroQuant is an AI-assisted program that compares your brain images to a normal population to determine volumetric changes as well as to show possible improvements from drug therapies or other forms of treatment.
The additional neuroquant sequences add no more than about 6 minutes to your exam, but they provide a wealth of information about your brain health. This program targets areas in the brain for:
Brain age/dementia/alzheimer's changes multiple sclerosis (changes, improvements) traumatic brain injury and the areas affected
Seizure/epileptic changes in the temporal lobes
Brain tumors and the areas of the brain affected by tumor, edema, radiation, etc.
Brain development in adolescents and developmentally-challenged adults covid-related changes
If you have a family history of dementia or alzheimer's or a personal history of any of the aforementioned anomalies, you qualify for the exam. Even if you are asymptomatic, this scan can provide baseline information, as future exams will be directly compared to your own NeuroQuant imaging studies to identify changes in your brain structure volume.
Most insurances pay for this additional imaging.
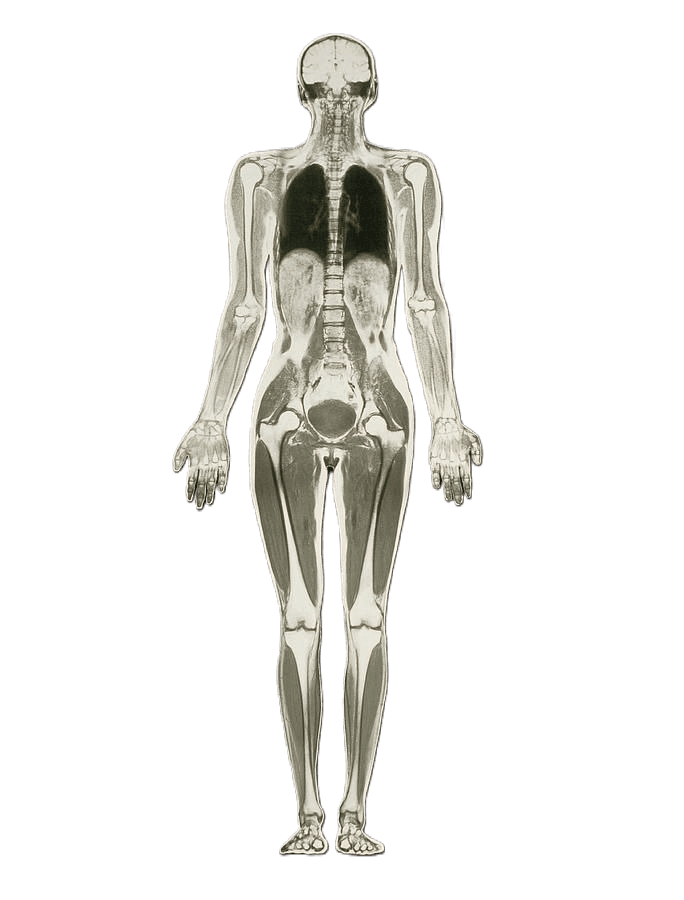
Whole Body MRI
Whole Body MRI is an imaging technique that utilizes MRI scans of large areas of the body to acquire multiple structures within one scan. A total of 4 scans are required to include the entire body, from head to foot.
There are many benefits in having a Whole Body MRI scan. One of the primary reasons is for cancer and precancer detection. Other uses of Whole Body MRI include:
Auto-Immune Diseases
Metabolic Diseases
Spine Disease
Kidney Disease
Brain Aneurysm
Arthritis
This scan takes approximately an hour, but the benefits are tremendous!
Insurance companies may not cover this scan, as it is considered a screening exam.